Introduction
In the previous part of this 3 part series, we looked at HSRP. Today we will look at VRRP, its features and how to configure it within Cisco IOS.
VRRP vs HSRP
VRRP is extremely similar to HSRP. However, unlike HSRP, VRRP is not Cisco proprietary.
Let us look at the differences between HSRP and VRRP:
| HSRP | VRRP | |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Cisco proprietary | IETF – RFC 3768 |
| Number of groups | 16 groups maximum | 255 groups maximum |
| Active/Standby | 1 active, 1 standby and multiple candidates | 1 active and several backups |
| Virtual IP Address | Different from real IP addresses on interfaces | Can be the same as the real IP address on an interface |
| Multicast Address | 224.0.0.2 | 224.0.0.18 |
| Tracking | Interfaces or Objects | Objects |
| Timers | Hello timer 3 seconds, hold time 10 seconds | Hello timer 1 second, hold time 3 seconds |
| Authentication | Supported | Not supported in RFC 3768 |
Table 1 : HSRP vs VRRP.[1]
Configuration
Now, we will configure VRRP, based on the diagram below. Furthermore, our VIP will be 10.0.128.10.
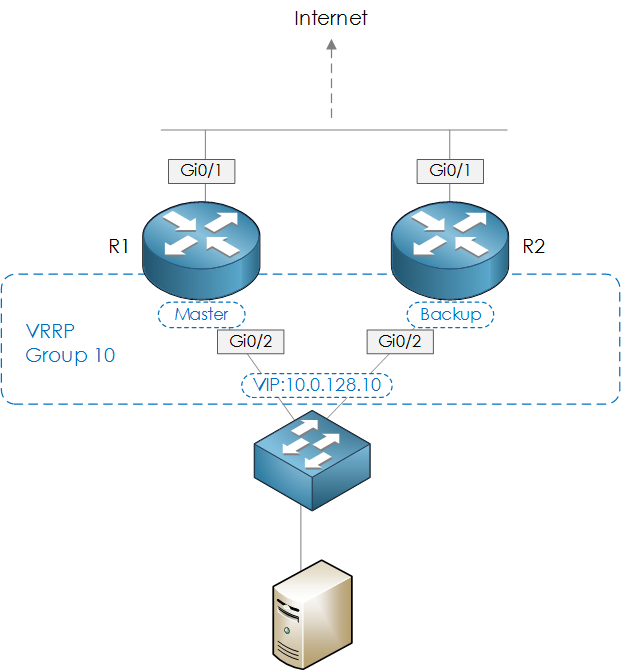
Figure 1 : Topology.
Initial Setup
R1
R1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/2
R1(config-if)# vrrp 10 ip 10.0.128.10
R1(config-if)# vrrp 10 priority 110
R2
R2(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/2
R2(config-if)# vrrp 10 ip 10.0.128.10
Verification
R1#show vrrp br
Interface Grp Pri Time Own Pre State Master addr Group addr
Gi0/2 10 110 3570 Y Master 10.0.128.1 10.0.128.10
Interface Tracking
Next, we will configure VRRP to track an interface, i.e the uplink interface (gi0/1). If the interface goes down then the VRRP priority will be decremented, in turn resulting in R2's priority to be higher and failover to occur.
R1
R1(config)# track 1 interface gi0/1 line-protocol
R1(config)#int gi0/2
R1(config-if)#vrrp 10 track 1 decrement 20
Verification
To confirm that this is configured correctly, we issue a shutdown on gi0/1.
We see the following output,
*May 7 05:19:46.809: %VRRP-6-STATECHANGE: Gi0/2 Grp 10 state Master -> Backup
Now, if we run a show VRRP we can see the expected output,
R1(config)# do show vrrp
GigabitEthernet0/2 - Group 10
State is Backup
Virtual IP address is 10.0.128.10
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.010a
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
*Priority is 90 (cfgd 110)*
*Track object 1 state Down decrement 20*
Master Router is 10.0.128.2, priority is 100
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.570 sec (expires in 3.243 sec)
Authentication
As the final step, we will configure authentication. This is a simple process of adding the VRRP authentication commands to each device and then verifying.
R1/R2
R1/R2(config-if)# vrrp 10 authentication md5 key-string VRRPPW
Verification
R1# show vrrp
GigabitEthernet0/2 - Group 10
State is Master
Virtual IP address is 10.0.128.10
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.010a
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
Priority is 110
Track object 1 state Up decrement 20
*Authentication MD5, key-string*
Master Router is 10.0.128.1 (local), priority is 110
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.570 sec
References
"VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) | NetworkLessons.com." 6 Oct. 2014, https://networklessons.com/cisco/ccie-routing-switching/vrrp-virtual-router-redundancy-protocol/. Accessed 8 May. 2018. ↩︎