What is an ASN?
An autonomous system number (ASN) is a unique number, assigned by IANA that is available globally to identify an autonomous system and which enables that system to exchange exterior routing information with other neighboring autonomous systems. [1]
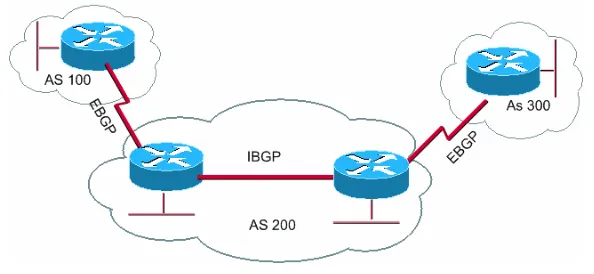
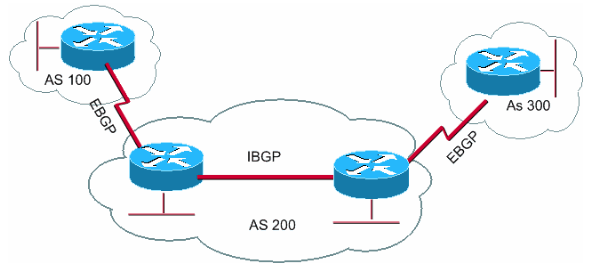
Figure 1 : BGP/ASN Example
ASN Types
There are two types of autonomous system numbers - public and private.
- Public ASN - Used when an AS is exchanging routing information with other Autonomous Systems on the public Internet. [2]
- Private ASN - Used if an AS is only required to communicate via Border Gateway Protocol with a single provider. As the routing policy between the AS and the provider will not be visible on the Internet. [3] In this case the upstream provider will typically remove the ASN from the ASN Path and replace it with his own public ASN. In reality, this can be thought of as a type of NAT for ASN`s.
ASN Ranges
Below lists the various ASN Ranges:
- 0 : reserved.
- 1-64,495 : public AS numbers.
- 64,496 – 64,511 : reserved to use in documentation.
- 64,512 – 65,534 : private AS numbers.
- 65,535 : reserved.
References
[1] "What is an Autonomous System Number (ASN)? - Definition from ...." https://www.techopedia.com/definition/26871/autonomous-system-number-asn . Accessed 2 Nov. 2017.
[2] "Autonomous System numbers – FAQs – APNIC." https://www.apnic.net/get-ip/faqs/asn/ . Accessed 2 Nov. 2017.
[3] "Autonomous System numbers – FAQs – APNIC." https://www.apnic.net/get-ip/faqs/asn/ . Accessed 2 Nov. 2017.